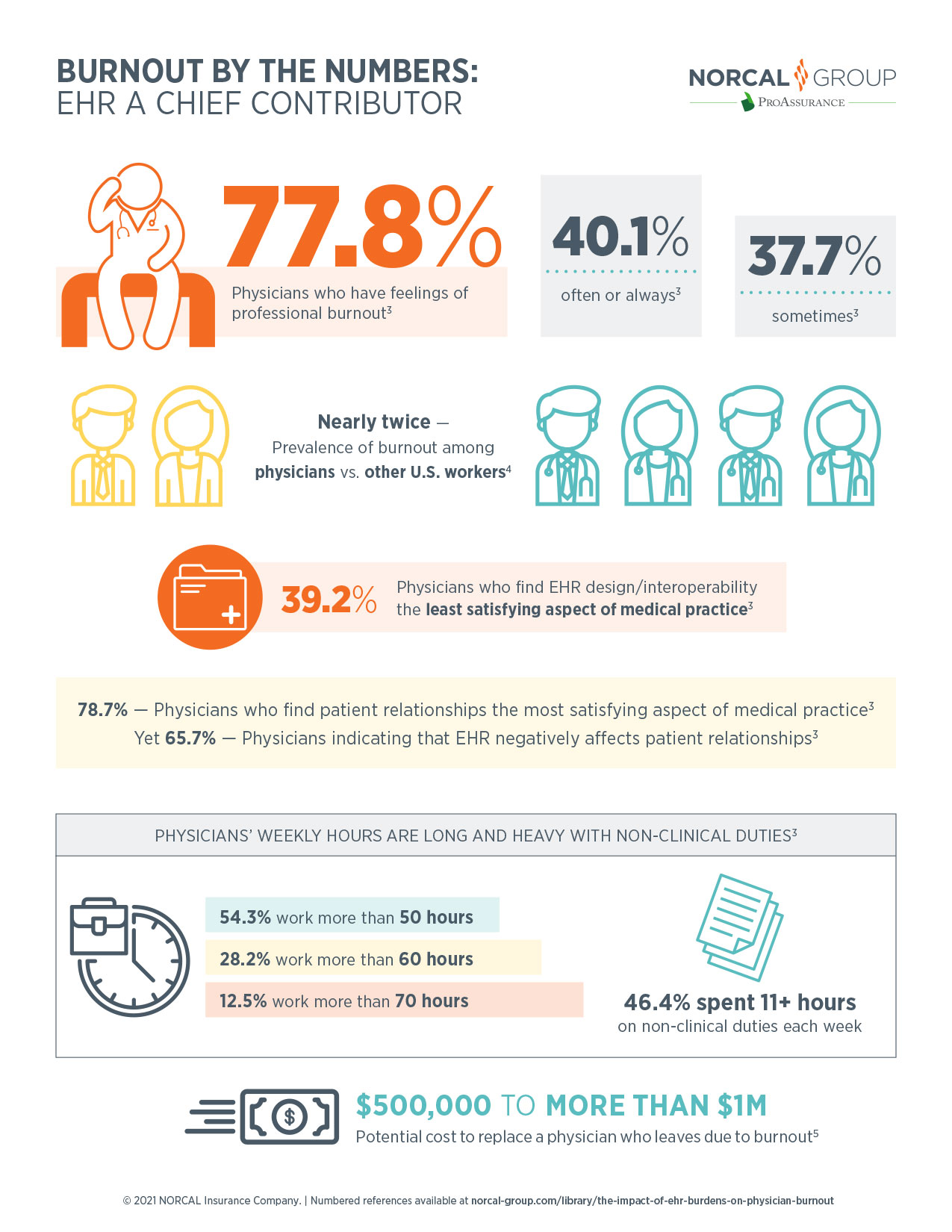
Physician burnout is associated with two-fold increased odds for unsafe care, unprofessional behaviors, and low patient satisfaction1 and that electronic health records (EHR) are a leading factor in physician burnout2.
The Challenges:
- 77.8% of physicians have feelings of professional burnout3
- Burnout is nearly twice as prevalent among physicians vs. other U.S. workers4
- 65.7% of physicians indicate that EHR negatively affects patient relationships3
- $500,000 to more than $1M potential cost to replace a physician who leaves due to burnout5
References
1. Maria Panagioti, PhD, et al. “Association Between Physician Burnout and Patient Safety, Professionalism, and Patient Satisfaction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.” JAMA Intern Med. 2018;178(10):1317–1330. doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2018.3713 (accessed 1/7/2019)
2. Tait D. Shanafelt, M.D., et al. “Relationship Between Clerical Burden and Characteristics of the Electronic Environment with Physician Burnout and Professional Satisfaction.” Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 2016;91(7):836-848. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2016.05.007 (accessed 1/7/2019)
3. The Physicians Foundation. 2018 Survey of America’s Physicians: Practice Patterns & Perspectives. 9/18/2018. (accessed 1/7/2019)
4. Lotte N. Dyrbye, et al. “Burnout Among Health Care Professionals: A Call to Explore and Address This Underrecognized Threat to Safe, High-Quality Care.” NAM Perspectives. 2017. Discussion Paper, National Academy of Medicine, Washington, DC. doi: 10.31478/201707b (accessed 1/7/2019)
5. Christine Sinsky, MD, FACP, et al. “Creating the Organizational Foundation for Joy in Medicine.” AMA, STEPS Forward. (accessed 1/7/2019)